Problem: MTU Size
The Maximum Transfer Unit (MTU) is the largest IP packet that can be accepted on a path, and is often as much as 1500 bytes in length. The maximum delay introduced by a packet is equivalent to the MTU size divided by the link speed - for example for T1 with a 1500 byte MTU the delay from one packet is 8 milliseconds. On link speeds of T1 rate or less the incremental delay caused by data packets causes jitter in voice packets, for example if two 1500 byte data packets are ahead of a voice packet then the voice will have to wait for 16 milliseconds before being transmitted.
Impact
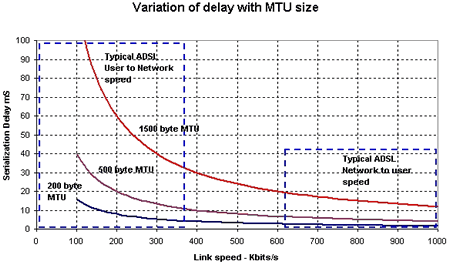
Low link speeds (under T1 rate) and large MTU sizes lead to increased levels of jitter, which in turn can lead to packet discard and degradation in voice quality. The chart below shows the variation of serialization delay (time taken to send a packet) with MTU size and link speed - jitter would generally occur as some multiple of this serialization delay.
Resolution
On link speeds of less than 512 kbits per second the MTU size should be limited to 512 bytes or less. Other approaches to resolving this problem include packet fragmentation and interleaving.
Tools:
Conditions of use: The material on this site is copyright VoIP Troubleshooter LLC and may be freely used but not copied or downloaded. In making use of this site the user acknowledges that VoIP Troubleshooter LLC or Contributor has no liability for any issues or problems that may arise directly or indirectly as a result of such use. VoIP Troubleshooter LLC and Contributor are providing this material as-is with no warranty as to correctness or completeness and do not accept any responsibility for any issues or problems of any nature whatsoever that may arise from the use of the material on this site.


